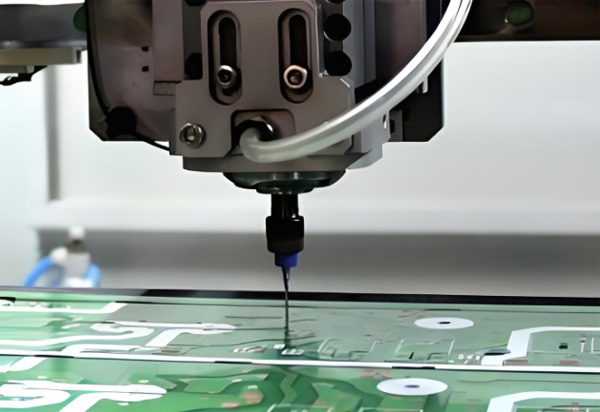
When I first started exploring industrial PCB production, I realized how complex and precise the process really is. From design and material selection to quality testing and certifications, every step matters. In this guide, I’ve gathered the common questions and clear answers to help anyone understand PCB manufacturing better.
Part 1. What is industrial PCB production?
Industrial PCB production is the large-scale process of designing, fabricating, and assembling printed circuit boards used in electronics. It involves advanced machinery, automated workflows, and strict quality control to ensure durability, precision, and performance in mass production.
Part 2. What are the main steps in PCB manufacturing?
The key steps include PCB design, material preparation, copper lamination, imaging and etching, drilling, plating, solder mask application, surface finish, silkscreen printing, electrical testing, and final cutting or panelization. Each step ensures accuracy and reliability of the circuit board.
Part 3. What materials are used in industrial PCB production?
Common materials include fiberglass-reinforced epoxy resin (FR4), copper foil, solder mask ink, and silkscreen ink. Advanced PCBs may use high-frequency laminates (e.g., Rogers, PTFE), flexible polyimide films, and specialty metals or coatings for specific applications.
Part 4. How are multilayer PCBs manufactured?
Multilayer PCBs are made by stacking alternating layers of copper and insulating materials, then pressing them under heat and pressure. The layers are bonded together with prepreg, followed by drilling, plating, and lamination to form electrical connections between layers.
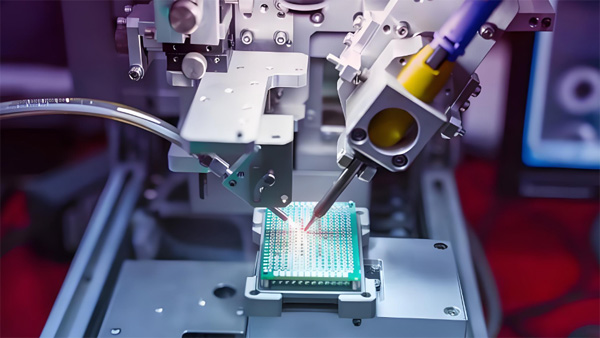
Part 5. What is the difference between prototype and mass PCB production?
Prototype PCB production focuses on small batches for design testing and validation, with higher flexibility and shorter turnaround. Mass production involves large-scale manufacturing optimized for cost efficiency, automation, and consistency across thousands of boards.
Part 6. How is quality control ensured in PCB manufacturing?
Quality control includes automated optical inspection (AOI), electrical testing, X-ray inspection, solderability tests, and adherence to IPC standards. Manufacturers also monitor processes such as plating thickness, alignment, and surface finish uniformity to ensure reliability.
Part 7. What are the common PCB surface finish types?
Surface finishes protect copper and enhance solderability. Common types include HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative), immersion tin, immersion silver, and hard gold plating for durability.
Part 8. How is solder mask applied during PCB production?
A liquid solder mask is coated onto the PCB surface, exposed to UV light through a photo tool, and developed to reveal pads and vias. It is then cured to form a protective layer that prevents solder bridges, oxidation, and environmental damage.
Part 9. What role does copper plating play in PCB manufacturing?
Copper plating creates conductive pathways in drilled holes and strengthens circuit traces. It ensures reliable electrical connections between layers in multilayer PCBs. The process typically involves electroplating to deposit uniform copper inside vias and on surfaces.
Part 10. How are PCBs tested before delivery?
PCBs undergo electrical testing to verify continuity and insulation resistance, AOI for detecting defects, flying probe tests for prototypes, and functional testing for assembled boards. These steps ensure the PCB meets design and performance specifications before shipment.
Part 11. FAQs about Industrial PCB Production
What is the typical lead time for industrial PCB production?
Lead time ranges from 5–10 days for standard PCBs, while complex multilayer or high-volume orders may take 2–4 weeks, depending on design, materials, and production capacity.
What factors affect PCB production costs?
Key factors include board size, layer count, material type, surface finish, order volume, lead time, and testing requirements. Complex designs or tight tolerances increase costs.
How are flexible PCBs manufactured?
Flexible PCBs use polyimide or polyester films as substrates. Circuits are etched onto the film, laminated, and coated with protective layers, allowing the board to bend or fold without damage.
What are the tolerances in industrial PCB production?
Typical tolerances include ±0.1 mm for drilling, ±10% for copper thickness, and ±0.075 mm for trace width/spacing. Advanced boards may require tighter tolerances for high-density designs.
How does panelization work in PCB manufacturing?
Panelization groups multiple PCBs into a single panel for efficient processing. V-scoring or breakaway tabs allow boards to be separated after assembly, reducing handling costs.
What are the environmental considerations in PCB production?
PCB manufacturing must manage chemical waste, heavy metals, and energy use. Eco-friendly practices include wastewater treatment, lead-free finishes, and recycling materials.
How do PCB manufacturers handle high-frequency boards?
They use low-loss materials like Rogers or PTFE, control impedance precisely, and apply strict design tolerances to minimize signal loss and electromagnetic interference.
What is the difference between FR4 and other PCB materials?
FR4 is a fiberglass epoxy laminate known for cost-effectiveness and durability. Alternatives like polyimide, Rogers, or metal-core materials are used for high-frequency, flexible, or high-power applications.
How is automation used in PCB production lines?
Automation handles drilling, imaging, plating, solder mask application, inspection, and testing. It improves precision, reduces labor costs, and boosts manufacturing speed and consistency.
What certifications are required for industrial PCB manufacturing?
Common certifications include ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environment), IATF 16949 (automotive), UL (safety), and IPC standards for PCB performance and reliability.
A professional with over a decade of experience in the PCB depaneling industry.