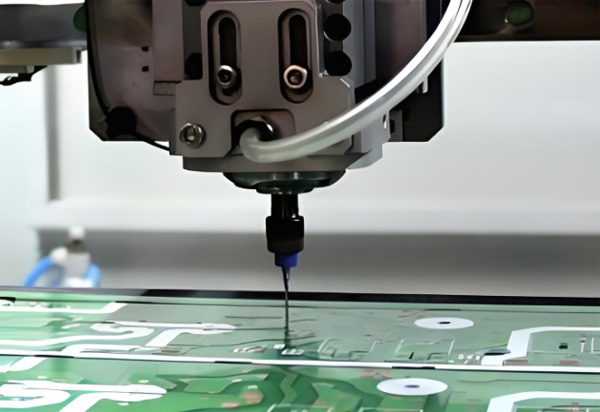
As someone who works with PCBs every day, I know how frustrating it can be when layers don’t line up correctly. That’s why pinner machines are so important—they’re the unsung heroes of PCB manufacturing. These simple but clever tools use alignment pins to lock layers in place, making sure every hole and trace lands exactly where it should. Let me explain how these machines work and why no PCB factory can really do without them.
- Part 1. What does pinner mean in PCB manufacturing?
- Part 2. What is a pinner machine used for in PCB production?
- Part 3. How does a PCB pinner work?
- Part 4. Why is pinner important in the PCB process?
- Part 5. What is the function of pinner in PCB drilling?
- Part 6. Is pinner used in multilayer PCB fabrication?
- Part 7. What types of pinner machines are used in PCB factories?
- Part 8. What’s the difference between pinner and pin registration in PCBs?
- Part 9. How does pinner improve PCB alignment accuracy?
- Part 10. What materials are used for pinner pins in PCB processing?
- Part 11. FAQS about PCB pinner
Part 1. What does pinner mean in PCB manufacturing?
In PCB manufacturing, a pinner is a machine or tool used to insert alignment pins through registration holes in PCB panels. It helps keep multiple PCB layers precisely aligned during processes like drilling or lamination.
Part 2. What is a pinner machine used for in PCB production?
A pinner machine is used to insert metal or plastic pins into the registration holes of PCB layers. This ensures that all layers stay perfectly aligned during stacking, drilling, or laminating, which is essential for multilayer PCB accuracy.
Part 3. How does a PCB pinner work?
A PCB pinner works by aligning drilled holes in stacked PCB sheets and inserting rigid pins through them. The machine typically uses optical alignment or mechanical guides to ensure precise positioning before pushing the pins in place.
Part 4. Why is pinner important in the PCB process?
The pinner is critical for maintaining layer-to-layer accuracy in multilayer PCBs. Misalignment during stacking or drilling can lead to defective vias or short circuits. Pinning keeps the layers steady and properly aligned throughout processing.

Part 5. What is the function of pinner in PCB drilling?
During drilling, the pinner ensures that stacked layers don’t shift. By using alignment pins, it locks the layers in position so that holes are drilled through the exact same point across all layers, ensuring proper via connectivity.
Part 6. Is pinner used in multilayer PCB fabrication?
Yes, pinners are commonly used in multilayer PCB fabrication. They are essential for stacking inner layers correctly before lamination and for keeping alignment consistent during mechanical drilling and hole plating processes.
Part 7. What types of pinner machines are used in PCB factories?
PCB factories use both manual and automatic pinner machines. Manual pinners require human alignment, while automatic pinners use cameras, sensors, and robotics for high-speed, precise pin insertion with minimal human intervention.
Part 8. What’s the difference between pinner and pin registration in PCBs?
“Pinner” refers to the machine or process of inserting alignment pins. “Pin registration” is the concept of using pins to achieve precise alignment between layers. Pin registration is the goal; a pinner is the tool used to achieve it.
Part 9. How does pinner improve PCB alignment accuracy?
By physically securing the PCB layers with alignment pins, a pinner eliminates shifting and skewing during drilling or lamination. This leads to more accurate via placement and trace routing, improving electrical performance and reliability.
Part 10. What materials are used for pinner pins in PCB processing?
Pinner pins are usually made of stainless steel or hardened steel for durability. In some cases, plastic pins are used when metal might damage delicate layers. The material must be hard, smooth, and precisely sized to prevent shifting or damage.
Part 11. FAQS about PCB pinner
How does pinner help with layer alignment in PCB lamination?
Pinner holds PCB layers together with alignment pins, keeping them properly stacked. This prevents shifting during lamination, ensuring accurate layer alignment and better board quality.
Do all PCB factories use pinner machines?
Most multilayer PCB factories use pinner machines. Single-layer or simple boards may skip it, but multilayer production relies on pinners for alignment.
How do you maintain a pinner machine in PCB production?
Regularly clean alignment pins, check calibration, lubricate moving parts, and replace worn pins. Routine checks help maintain alignment accuracy.
What are common problems with pinner in PCB manufacturing?
Common issues include worn pins, misalignment, bent boards, or debris in holes. Poor maintenance can lead to bad registration and defective boards.
Can pinner reduce PCB production defects?
Yes, pinners help reduce layer shift, drill misalignment, and electrical failures, lowering overall production defects in multilayer boards.
How does pinner affect PCB drilling precision?
By securing layers, pinner ensures drill holes align correctly across all layers, improving drilling precision and via reliability.
Are there automatic pinner systems for PCB lines?
Yes, many factories use automatic pinners with vision systems for fast, precise pinning, reducing manual labor and improving consistency.
What is manual pinner vs. automatic pinner in PCB process?
Manual pinners need human setup and alignment. Automatic pinners use machines to align and pin layers faster and more accurately.
How do you choose a suitable pinner machine for PCB production?
Choose based on PCB layer count, production scale, accuracy needs, and budget. High-volume plants often prefer automatic pinners.
What safety precautions are needed when using pinner in PCB fabrication?
Wear gloves, avoid loose clothing, follow lock-out procedures, and keep hands clear of moving parts. Regular training ensures safe operation.
A professional with over a decade of experience in the PCB depaneling industry.