When I first heard about PCB board coating, I thought it was just an extra step — but it’s actually key to keeping circuit boards safe. This thin protective layer shields PCBs from moisture, dust, and heat, helping them last longer and work better. In this simple guide, I’ll answer the most common questions about PCB coating, including what it is, how it’s applied, and why it matters.
Part 1. What is PCB coating and why is it important?
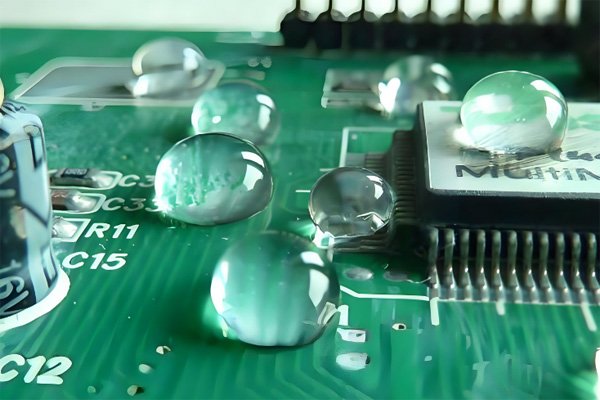
PCB coating, also called conformal coating, is a thin protective layer applied to printed circuit boards. It protects the board from moisture, dust, chemicals, and temperature changes. This coating helps prevent corrosion, short circuits, and electrical leakage, ensuring long-term reliability and performance in harsh environments.
Part 2. What types of conformal coatings are used for PCBs?
Common types include acrylic, silicone, polyurethane (urethane), epoxy, and parylene. Acrylic coatings are easy to apply and remove, silicone offers great flexibility and high-temperature resistance, polyurethane provides strong chemical protection, epoxy is highly durable, and parylene gives uniform coverage even in tight spaces.
Part 3. How does PCB conformal coating protect electronic boards?
Conformal coating acts as an insulating barrier that shields the PCB from environmental factors like moisture, salt, and dust. It prevents corrosion, electrical leakage, and damage from vibration or thermal stress. The coating also helps reduce arcing between conductors, extending the board’s lifespan and maintaining consistent performance.
Part 4. What materials are used for PCB coating (acrylic, silicone, urethane, etc.)?
Acrylic coatings are popular for their easy application and repair. Silicone coatings resist heat and moisture well. Urethane coatings protect against chemicals and abrasion, while epoxy coatings are tough and ideal for extreme conditions. Parylene coatings provide a uniform, pinhole-free layer with excellent dielectric strength.

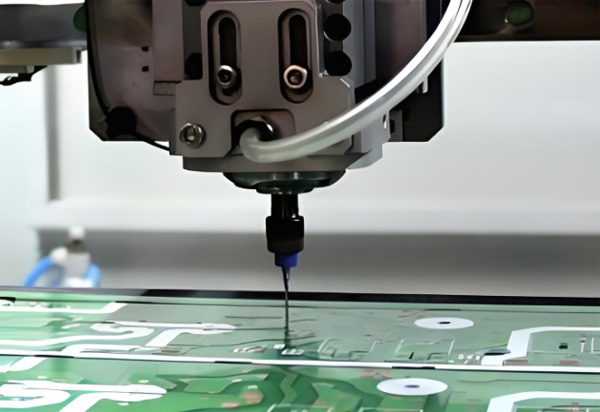
Part 5. How is PCB coating applied?
PCB coatings can be applied by brushing, dipping, spraying, or automated selective coating. Brushing works for small touch-ups, dipping ensures full coverage, and spraying offers an even finish. In mass production, robotic systems selectively coat areas while avoiding connectors or sensitive components.
Part 6. What is the difference between conformal coating and potting?
Conformal coating is a thin, lightweight film that covers the PCB surface, while potting completely encapsulates the board in a thick resin layer. Coating provides flexibility and easy rework, whereas potting offers stronger protection against impact, vibration, and harsh chemicals but adds weight and reduces accessibility.
Part 7. How thick should a PCB coating layer be?
Typical conformal coating thickness ranges from 25 to 250 microns (0.025–0.25 mm), depending on the material type and application method. Thinner coatings are used for low-voltage electronics, while thicker layers offer better protection for high-stress environments. Uniform thickness ensures proper insulation and durability.
Part 8. Can I apply PCB coating at home?
Yes, small PCB coatings can be applied at home using aerosol sprays or brush-on types. Make sure to clean the board thoroughly, mask off connectors, and work in a ventilated area. Apply thin, even coats and allow proper drying or curing time. However, professional coatings offer more precision and durability.
Part 9. How do I remove or repair damaged PCB coating?
You can remove coating using chemical solvents (for acrylics or urethanes), gentle heat, or mechanical scraping depending on the type. To repair small areas, clean the damaged spot, apply new coating, and cure it properly. Always use compatible materials to maintain insulation and protection levels.
Part 10. What are common problems or defects in PCB coating?
Typical coating issues include bubbles, uneven thickness, poor adhesion, or missed spots. These usually result from improper cleaning, incorrect viscosity, or inadequate curing. Contamination on the PCB surface can also cause coating defects. Regular inspection and controlled application conditions help prevent these problems.
Part 11. FAQs about PCB Coating
How do you inspect or test PCB coating quality?
PCB coatings are checked using visual inspection, UV light (since most coatings fluoresce), and thickness measurement tools. Advanced methods include adhesion tests, cross-section analysis, and environmental stress testing to ensure uniform coverage, proper adhesion, and reliable protection.
Is PCB coating waterproof or moisture-resistant?
Yes, conformal coatings are moisture-resistant but not fully waterproof. They protect against humidity, condensation, and splashes but can’t withstand full water immersion. For complete waterproofing, potting or encapsulation methods are used instead of standard conformal coatings.
What industries commonly use PCB conformal coatings?
Conformal coatings are widely used in aerospace, automotive, marine, military, medical, and consumer electronics. These industries rely on coatings to protect circuit boards from harsh environments, vibration, chemicals, and temperature extremes, ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
How does temperature or humidity affect PCB coating performance?
Extreme heat can cause coating softening, cracking, or delamination, while high humidity may reduce adhesion or cause moisture ingress over time. Choosing temperature-resistant materials like silicone or parylene helps maintain performance in demanding or humid environments.
What are the best PCB coating methods for high-reliability applications?
For critical applications, parylene coating and selective robotic spraying are best. Parylene offers uniform, pinhole-free protection with strong dielectric strength. Automated spraying ensures consistency and precision, making both methods ideal for aerospace, military, and medical electronics.